by Sonam Srivastava
Published On June 8, 2024
The 2024 elections have ushered in a new era for India, with the BJP-led NDA coalition forming the government for a third consecutive term. As the dust settles on a tumultuous election season, investors are keenly assessing the potential impact on Indian equities over the next five years. This period is poised to be transformative, with significant implications for market confidence and investment strategies.
The BJP's coalition government, though lacking a clear majority, brings a mix of continuity and change. The anticipated increase in welfare spending, particularly focused on rural areas, signals a shift towards addressing voter concerns about rural distress. This move is expected to stimulate demand in various sectors, from consumer goods to agriculture-related industries.
However, the coalition dynamics also suggest potential challenges in policy implementation, especially in areas requiring state cooperation, such as power and GST reforms. These complexities could influence the regulatory environment and affect investor sentiment.
Another critical aspect is the government's ongoing emphasis on expanding manufacturing and improving employment rates. Initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme are likely to receive continued support, potentially boosting sectors like electronics and pharmaceuticals.
In this blog, we explore how these political developments will shape the trajectory of Indian equities. From sectoral impacts to broader economic trends, we analyze the factors that will drive market confidence and offer insights on navigating this evolving landscape. Join us as we delve into the future of Indian equities in the post-2024 election era, providing a roadmap for investors seeking to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
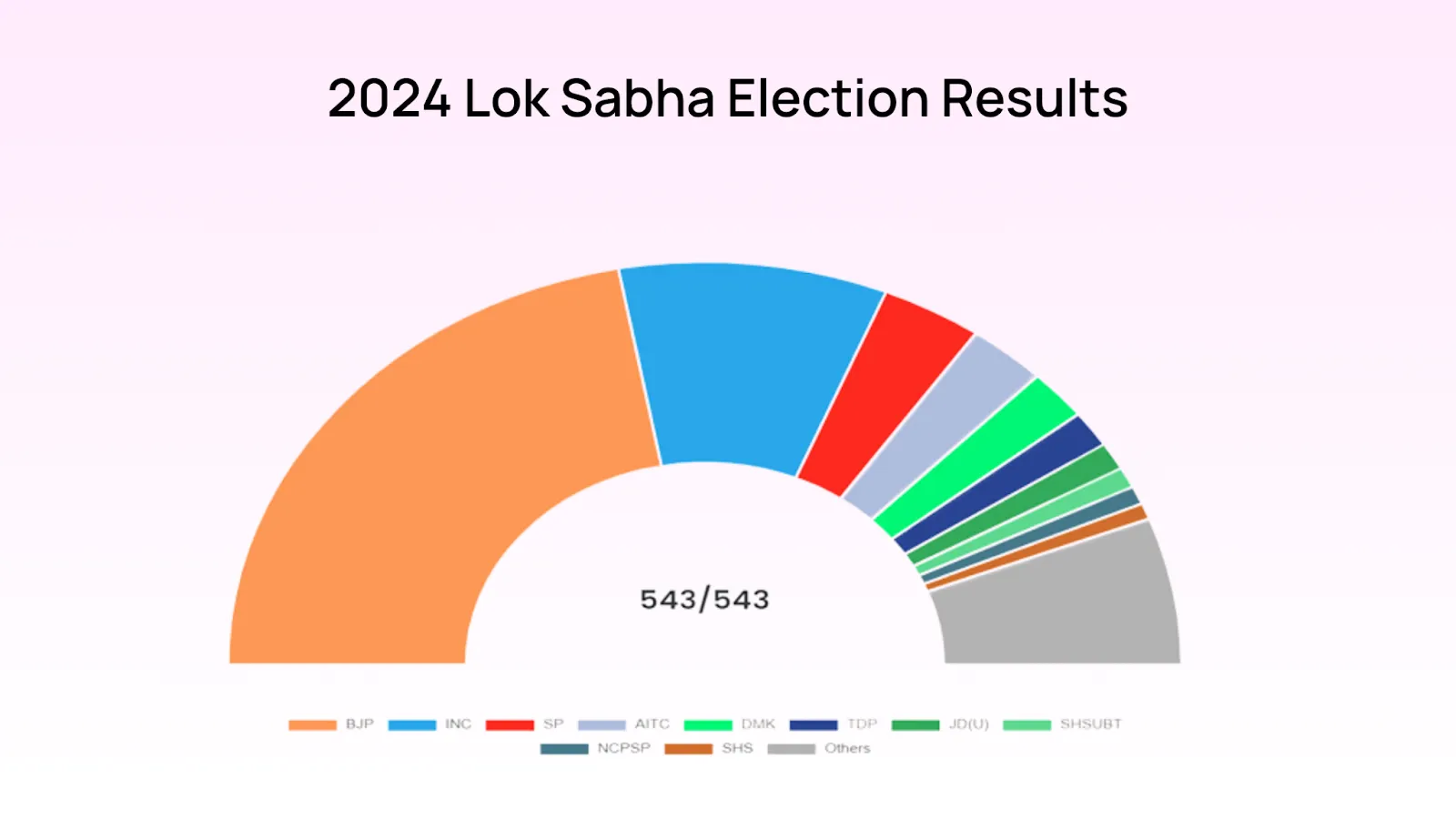
The 2024 elections have been a defining moment in India's democratic journey, marked by intense political campaigns, high voter turnout, and significant changes in the political landscape. The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, once again emerged as a key player, but this time with a nuanced victory. While the BJP did not secure an outright majority, it successfully formed the government through a coalition with the National Democratic Alliance (NDA), securing approximately 292 seats in the Lok Sabha.
This coalition victory highlights the diverse and fragmented nature of Indian politics, where regional parties have gained substantial influence. The BJP's performance saw a decline in the number of seats compared to the 2019 elections, losing around 63 seats. This loss can be attributed to various factors, including rural distress, economic challenges, and a strong opposition campaign.
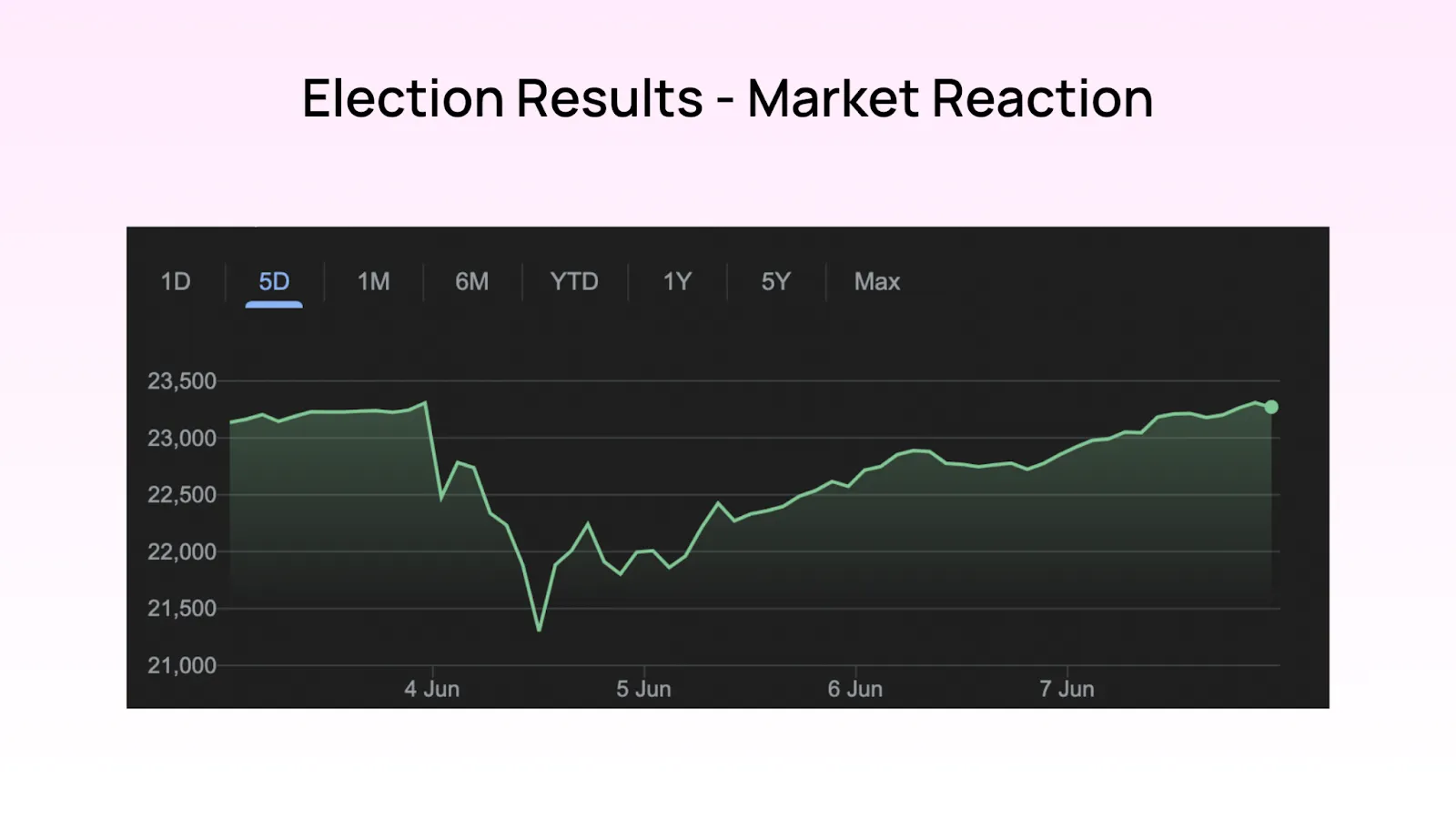
The election results had an immediate impact on market sentiment. Initially, the markets exhibited volatility as investors processed the implications of a coalition government. The absence of a clear majority raised concerns about potential policy gridlock and slower decision-making processes. However, the fact that the BJP-led NDA could form the government provided a sense of continuity and stability, which gradually calmed investor nerves.
Key sectors such as banking, infrastructure, and consumer goods reacted positively, anticipating continued reforms and policy support. On the other hand, sectors dependent on swift legislative action, like power and GST reforms, faced uncertainty. The market's reaction underscored the importance of stable governance and effective policy implementation in maintaining investor confidence.
To understand the significance of the 2024 election outcomes, it is essential to compare them with previous election cycles. In the 2014 and 2019 elections, the BJP achieved decisive victories, securing clear majorities that allowed for bold policy initiatives and reforms. These victories were characterized by strong mandates that enabled the government to implement significant economic and structural changes, including the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and various infrastructure projects.
In contrast, the 2024 elections reflect a more fragmented mandate, with the BJP needing to rely on coalition partners to form the government. This scenario is reminiscent of the early 2000s when coalition politics was the norm, and governments had to navigate through complex alliances to implement policies. The current political landscape suggests that while the BJP remains a dominant force, regional parties have strengthened their positions, necessitating a more collaborative approach to governance.
The 2024 election results have resulted in a coalition government led by the BJP and supported by the National Democratic Alliance (NDA). Coalition governments, by their very nature, bring both challenges and opportunities.
Consensus Building: One of the primary challenges is the need to build consensus among coalition partners, each with their own regional interests and political agendas. This can slow down the decision-making process and lead to compromises that dilute policy effectiveness.
Policy Continuity: Maintaining policy continuity can be difficult when coalition partners have differing views on key issues. This can create uncertainty and instability, which might deter investment and hinder economic progress.
Political Stability: The stability of the government itself can be a concern. Coalition governments are often susceptible to internal conflicts and the risk of partners withdrawing support, which can lead to political instability and frequent changes in leadership.
Implementation Delays: Large-scale reforms and infrastructural projects might face delays due to prolonged negotiations and the need to appease multiple stakeholders.
Inclusive Governance: A coalition government can promote more inclusive governance by representing a broader spectrum of regional and local interests. This can lead to policies that are more attuned to the needs of diverse communities across the country.
Collaborative Policy Making: The necessity to collaborate can foster innovative and well-rounded policy solutions. When multiple viewpoints are considered, the resulting policies may be more comprehensive and sustainable.
Regional Development: Coalition partners often bring a strong focus on regional development. This can lead to targeted initiatives that address specific local needs, potentially reducing regional disparities and promoting balanced economic growth.
Policy Frictions:
Economic Reforms: Economic reforms such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and labor laws may face resistance from coalition partners who are wary of their impact on regional economies. Balancing national interests with regional concerns will be a delicate task.
Agricultural Policies: Different states have varying agricultural priorities, which can lead to conflicts over policies related to subsidies, pricing, and rural development. Coalition partners from agrarian states may push for more favorable terms, creating friction with the central leadership.
Social Policies: Social policies, including education, health, and welfare, can also be contentious. Coalition partners may have different priorities and approaches to addressing social issues, leading to disagreements and compromises.
Infrastructure Projects: Large infrastructure projects often require land acquisition and environmental clearances, which can be contentious. Different coalition partners may have varying stances on these issues, leading to delays and modifications in project plans.
Areas of Cooperation:
Rural Development: Given the significant losses the BJP experienced in rural areas, there is likely to be a strong focus on rural development. Coalition partners, especially those representing rural constituencies, can work together to formulate and implement policies aimed at alleviating rural distress and boosting agricultural productivity.
Manufacturing and Employment: There is a broad consensus on the need to expand manufacturing and create jobs. Initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme are likely to receive support from all coalition partners, leading to cooperative efforts to boost industrial growth.
Healthcare and Education: Improving healthcare and education is a priority that transcends political divides. Coalition partners can collaborate to enhance public health infrastructure and educational outcomes, benefiting the population at large.
Environmental Sustainability: Environmental issues such as clean energy, waste management, and climate resilience are areas where coalition partners can find common ground. Collaborative efforts can lead to sustainable policies that address both economic and environmental concerns.
The 2024 election results have highlighted a crucial need for the government to address the growing concerns of rural distress and economic disparities. In response, the newly formed BJP-led NDA government is expected to significantly increase welfare spending. This strategic move aims to alleviate rural distress, stimulate economic activity, and restore confidence among rural voters who felt neglected in previous years.
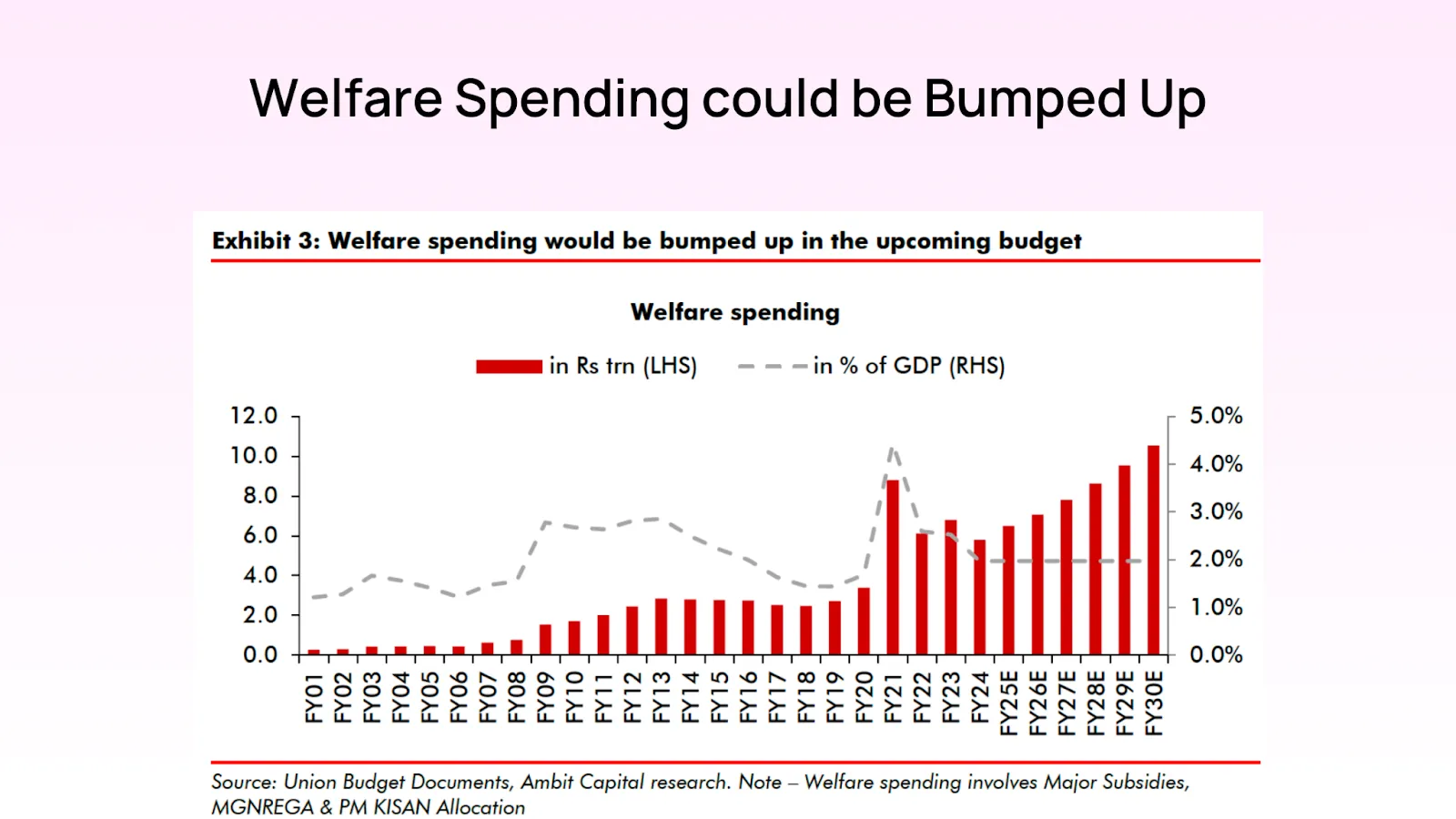
Budget Allocation: It is anticipated that the government will raise welfare spending from the previous level of 1.6% of GDP to 2%. This represents a substantial increase in budget allocation, amounting to an additional Rs 1.2 trillion.
Targeted Programs: The focus will be on targeted welfare programs that directly impact rural households. This includes enhancements to existing schemes like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) and the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN).
Direct Benefit Transfers: Expanding the scope and efficiency of direct benefit transfers (DBT) will ensure that subsidies and financial aid reach the intended beneficiaries promptly and without leakages.
Health and Education: Investment in rural health and education infrastructure is likely to be prioritized. This includes building more health centers, improving school facilities, and launching nutrition programs for children and pregnant women.
The election results underscored the significant voter dissatisfaction stemming from rural distress, which was exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The government's strategy to address these issues will be multifaceted, aiming not only to provide immediate relief but also to foster long-term economic recovery in rural areas.
Components of the Focus on Rural Distress:
Agricultural Support: Increasing minimum support prices (MSPs) for key crops, providing crop insurance, and offering subsidies on fertilizers and seeds will help mitigate the financial risks faced by farmers.
Infrastructure Development: Developing rural infrastructure, including roads, irrigation systems, and digital connectivity, will enhance productivity and access to markets, thereby boosting rural economies.
Microfinance and Credit Access: Expanding microfinance programs and improving access to credit for small and marginal farmers will empower them to invest in better farming techniques and equipment.
Skill Development: Initiatives aimed at skill development and vocational training will prepare the rural workforce for diverse employment opportunities beyond agriculture, promoting inclusive growth.
The anticipated increase in welfare spending and focus on rural economic recovery will have a ripple effect across various sectors, driving growth and investment opportunities.
1. Agriculture and Allied Sectors:
Farm Equipment Manufacturers: Companies producing tractors, harvesters, and other agricultural machinery will see increased demand as farmers invest in modern equipment.
Fertilizers and Agrochemicals: Enhanced support for crop inputs will boost sales for companies in the fertilizers and agrochemicals sectors.
Irrigation Solutions: Firms providing irrigation technology and solutions will benefit from government initiatives to improve water management in agriculture.
2. Consumer Goods:
Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG): Increased rural incomes and direct benefit transfers will lead to higher consumption of FMCG products, benefiting companies in this sector.
Durables and Electronics: As rural households gain more purchasing power, the demand for consumer durables, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and televisions, is expected to rise.
3. Financial Services:
Microfinance Institutions: With a focus on improving credit access, microfinance institutions will play a pivotal role in providing financial services to rural communities, driving their growth.
Banks: Banks with strong rural outreach will benefit from increased deposits and loan disbursements, particularly those engaged in agricultural finance and rural development schemes.
4. Infrastructure and Construction:
Rural Roads and Connectivity: Companies involved in the construction of rural roads, bridges, and digital infrastructure will see new opportunities as the government prioritizes connectivity.
Housing: With better economic conditions, demand for rural housing and related construction materials is likely to increase, benefiting construction firms and material suppliers.
5. Healthcare and Education:
Healthcare Providers: Investments in rural healthcare infrastructure will drive demand for medical equipment, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare services in rural areas.
Education Services: Companies providing educational resources, digital learning tools, and infrastructure development for schools will benefit from increased spending on rural education.
The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, introduced by the Indian government, aims to boost domestic manufacturing, increase employment opportunities, and enhance the global competitiveness of Indian industries. The 2024 election results reinforce the government's commitment to expanding this scheme to drive economic growth and create jobs.
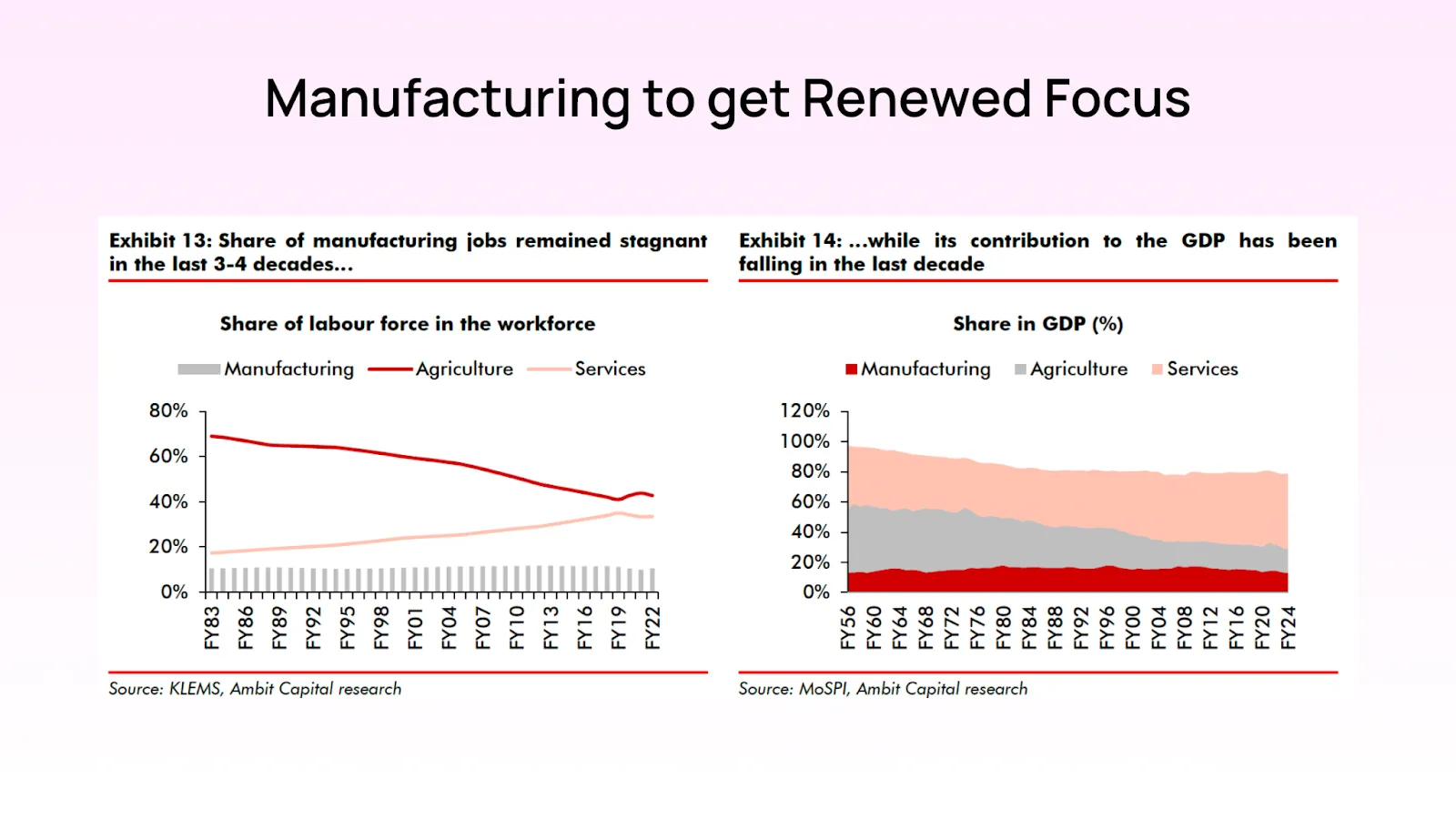
Key Aspects of the PLI Scheme Expansion:
Increased Budget Allocation: The government is expected to allocate additional funds to the PLI scheme, extending its coverage to more sectors. This will provide financial incentives to companies that achieve incremental production targets.
Wider Sector Inclusion: Originally focused on a few key sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, the PLI scheme's expansion will likely include more industries like textiles, food processing, and renewable energy. This broadens the impact of the scheme across the economy.
Incentive Structures: The scheme will offer various forms of incentives, such as tax rebates, subsidies, and easier access to credit, encouraging companies to invest in expanding their manufacturing capacities.
Monitoring and Evaluation: The government will implement robust mechanisms to monitor the performance of beneficiaries, ensuring that the incentives lead to tangible increases in production and employment.
The new government is set to prioritize strategies that bolster the manufacturing sector and generate employment, recognizing these as critical for economic stability and growth.
1. Infrastructure Development:
Industrial Corridors: Developing industrial corridors and special economic zones (SEZs) will provide the necessary infrastructure and logistical support for manufacturing units. Projects like the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) will play a crucial role in this strategy.
Transportation Networks: Improving transportation networks, including highways, railways, and ports, will reduce logistics costs and enhance the efficiency of supply chains.
2. Ease of Doing Business:
Regulatory Reforms: Simplifying regulatory processes, reducing red tape, and ensuring faster clearances will attract both domestic and foreign investments in the manufacturing sector.
Single-Window Clearance: Implementing a single-window clearance system for industrial projects will streamline approvals and reduce the time required to start new ventures.
3. Skill Development and Vocational Training:
Training Programs: Expanding vocational training programs and skill development initiatives will ensure that the workforce is equipped with the skills needed for modern manufacturing jobs. Partnerships with industry and educational institutions will be crucial in this regard.
Apprenticeship Programs: Encouraging companies to adopt apprenticeship programs will provide hands-on experience to young workers, bridging the gap between education and employment.
4. Technological Upgradation:
Adoption of Industry 4.0: Promoting the adoption of advanced technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will enhance productivity and innovation in the manufacturing sector.
Research and Development (R&D): Increasing investment in R&D will drive innovation and help Indian manufacturers develop cutting-edge products that can compete globally.
Several industries are expected to benefit significantly from the government’s initiatives to boost manufacturing and employment. These industries are likely to see increased investment, technological advancements, and job creation.
1. Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing:
Consumer Electronics: The demand for consumer electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and home appliances is on the rise. The PLI scheme will incentivize companies to ramp up production and meet both domestic and export demands.
Semiconductors: Recognizing the strategic importance of semiconductor manufacturing, the government will focus on building a robust semiconductor ecosystem, including chip design and fabrication units.
2. Automotive and Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Traditional Automotive: The automotive industry will continue to benefit from incentives aimed at increasing production capacities and adopting new technologies. This includes both passenger and commercial vehicles.
Electric Vehicles: With a global shift towards green energy, the production of electric vehicles and related components, such as batteries and charging infrastructure, will receive significant support.
3. Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology:
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: The PLI scheme will support the expansion of pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring a stable supply of essential medicines and fostering innovation in drug development.
Biotechnology: Investment in biotechnology, including vaccine production and biotech research, will be encouraged, positioning India as a hub for biotech innovation.
4. Renewable Energy and Green Technologies:
Solar and Wind Energy: The government will promote the manufacturing of solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy equipment, aiming to reduce reliance on imports and boost green energy production.
Green Technologies: Investment in green technologies such as energy-efficient appliances, electric grids, and sustainable building materials will be prioritized.
5. Textiles and Apparel:
Textile Manufacturing: The expansion of the PLI scheme to include textiles will enhance production capabilities, improve quality, and boost exports. This sector is labor-intensive and holds significant potential for job creation.
Technical Textiles: The focus will also extend to technical textiles, which have applications in various industries, including healthcare, automotive, and construction.
6. Food Processing:
Agricultural Products: The food processing industry will benefit from incentives to enhance the value addition of agricultural products, reduce wastage, and improve supply chain efficiencies.
Processed Foods: Expanding the production of processed foods for both domestic consumption and export will drive growth in this sector.
Read this article to know - Top 5 Growing Sectors to Invest in India 2024
Current State: The FMCG sector has traditionally been a resilient performer in the Indian market, driven by steady demand for essential products such as food, beverages, personal care, and household items. Despite economic fluctuations, FMCG companies have maintained consistent growth due to their broad consumer base.
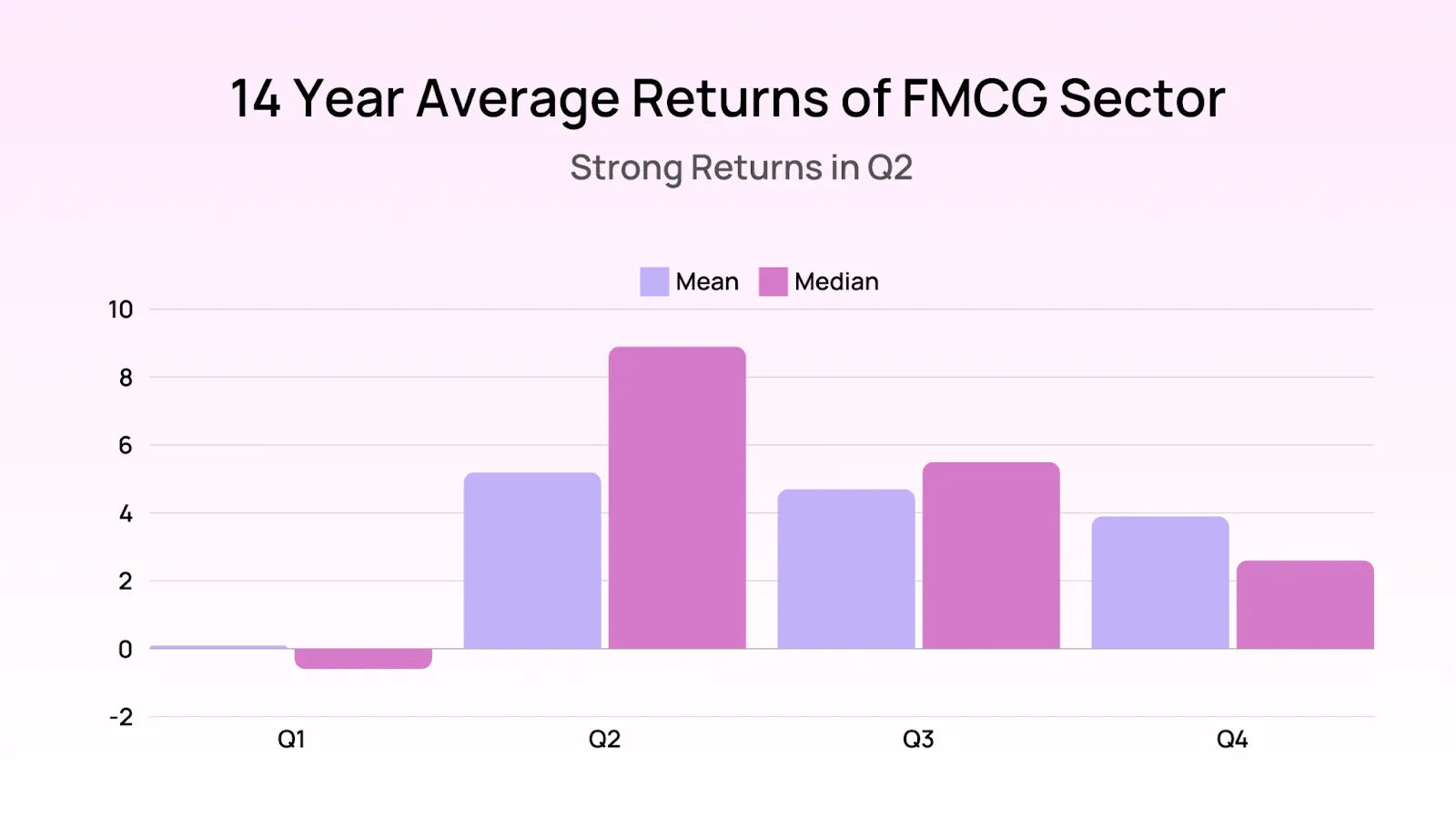
Growth Drivers:
Rural Demand: Increased welfare spending and direct benefit transfers are expected to boost rural incomes, leading to higher consumption of FMCG products in rural areas.
Urbanization: Rising urbanization and increasing disposable incomes in urban areas continue to drive demand for premium and branded products.
E-commerce: The expansion of e-commerce platforms has made FMCG products more accessible, especially in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Investment Opportunities:
Diversified Portfolios: Companies with diversified product portfolios and strong distribution networks are well-positioned to capture growth across different market segments.
Innovation: Firms that innovate and introduce new products catering to changing consumer preferences are likely to outperform.
Current State: The banking sector plays a crucial role in the Indian economy, encompassing both public and private sector banks. The sector has faced challenges such as non-performing assets (NPAs) and regulatory changes but remains pivotal for economic growth.
Growth Drivers:
Credit Growth: An expected revival in credit demand from both retail and corporate segments will drive growth. Increased lending to MSMEs and rural areas will also contribute.
Digital Transformation: The adoption of digital banking services, including mobile banking and fintech innovations, is enhancing operational efficiency and customer reach.
Regulatory Support: Government initiatives aimed at improving financial inclusion and restructuring stressed assets will support sectoral growth.
Investment Opportunities:
Large-Cap Banks: Banks with strong balance sheets, extensive branch networks, and robust digital capabilities are attractive investments.
Niche Players: Specialized banks focusing on segments such as housing finance, SME lending, and rural banking present unique growth opportunities.
Current State: Infrastructure development is a key focus area for the Indian government, encompassing sectors like transportation, energy, urban development, and digital infrastructure.
Growth Drivers:
Government Initiatives: Massive government spending on infrastructure projects, including the construction of highways, railways, ports, and smart cities, will drive sector growth.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Increased emphasis on PPPs will bring in private investment and expertise, accelerating project execution and efficiency.
Sustainable Development: Initiatives focused on renewable energy and sustainable urban planning will attract investments in green infrastructure projects.
Investment Opportunities:
Construction and Engineering Firms: Companies involved in large-scale infrastructure projects, including construction, engineering, and project management, are poised for growth.
Renewable Energy: Firms specializing in renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar and wind power, will benefit from the shift towards sustainable energy sources.
Sector Rotations: Sector rotations refer to the strategic shifting of investments from one sector to another based on economic cycles, policy changes, and market conditions. In the post-2024 election scenario, investors should consider the following sector rotations:
From Defensive to Cyclical: With increased government spending and economic recovery, investors might rotate from defensive sectors like FMCG and healthcare to cyclical sectors like infrastructure, real estate, and industrials.
From Traditional Energy to Renewable Energy: As the government pushes for sustainable development, investments may shift from traditional energy sectors like oil and gas to renewable energy sectors.
From Large-Cap to Mid-Cap and Small-Cap: With improving economic conditions and policy support, mid-cap and small-cap stocks might offer higher growth potential compared to large-cap stocks.
Strategic Investment Positions:
Overweight on Infrastructure and Capital Goods: Given the government's focus on infrastructure development, taking an overweight position in infrastructure and capital goods sectors can capitalize on expected growth.
Selective Banking Exposure: Focusing on banks with strong digital capabilities and niche market strategies can provide stable returns amid evolving financial landscapes.
Investing in Green Technologies: Allocating investments to companies involved in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and sustainable technologies aligns with global and domestic trends towards sustainability.
Current State: India's IT sector is globally recognized for its software services and outsourcing capabilities. The sector has shown resilience and adaptability, driving significant economic contributions.
Growth Drivers:
Digital Transformation: Increased digital adoption across industries, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity, will drive demand for IT services.
Global Outsourcing: Continued demand for cost-effective IT solutions from global clients will sustain the growth momentum.
Innovation and R&D: Investments in innovation and research and development (R&D) will help Indian IT firms stay competitive and expand their service offerings.
Investment Opportunities:
Large IT Firms: Established IT giants with a diversified global client base and strong financials are safe investment bets.
Emerging Tech Companies: Smaller firms specializing in cutting-edge technologies and niche services present high-growth potential.
Current State: The pharmaceutical and healthcare sector is critical for India, known for its generic drug manufacturing and significant contributions to global healthcare.
Growth Drivers:
Aging Population: An aging population and increasing healthcare awareness will drive demand for medical services and pharmaceuticals.
Healthcare Infrastructure: Government initiatives to improve healthcare infrastructure, especially in rural areas, will boost the sector.
Research and Development: Increased focus on R&D and innovation in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals will enhance the sector's growth prospects.
Investment Opportunities:
Generic Drug Manufacturers: Companies with strong capabilities in generic drug production and global exports are poised for growth.
Healthcare Service Providers: Firms involved in hospital management, diagnostics, and telemedicine will benefit from expanding healthcare infrastructure.
Current State: The real estate sector has experienced cycles of boom and bust but remains a significant contributor to the economy, driven by urbanization and housing demand.
Growth Drivers:
Affordable Housing: Government initiatives to promote affordable housing will drive growth in the residential real estate segment.
Commercial Real Estate: Demand for commercial spaces, including offices and retail outlets, will increase as economic activities pick up.
Smart Cities: Development of smart cities and urban renewal projects will create opportunities in the real estate sector.
Investment Opportunities:
Residential Developers: Companies focusing on affordable and mid-segment housing projects will benefit from policy support and increasing demand.
Commercial Real Estate Firms: Developers of commercial properties, including office spaces and malls, are poised for growth as the economy recovers.
The 2024 election results have ushered in a period of both opportunities and challenges for the Indian economy and equity markets. The BJP-led NDA coalition government, while lacking an outright majority, signals a need for strategic governance and collaborative policy-making. This political landscape will significantly impact various sectors, shaping investment opportunities and market performance over the next five years.
Key Points:
Election Outcomes and Market Sentiment: The formation of the coalition government has led to initial market volatility, with investors cautiously optimistic about the continuity and stability promised by the BJP-led NDA.
Coalition Dynamics: The coalition government presents both challenges in terms of policy implementation and opportunities for inclusive governance. Building consensus among diverse partners will be crucial for effective policy-making.
Welfare Spending and Rural Economic Stimulus: The government is expected to increase welfare spending, focusing on alleviating rural distress and stimulating economic recovery. Key sectors like FMCG, agriculture, and rural infrastructure stand to benefit significantly.
Manufacturing and Employment Initiatives: Expansion of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and other strategies to boost manufacturing and job creation will drive growth in industries such as electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy.
Sectoral Analysis and Investment Opportunities: Detailed sectoral analysis highlights promising investment opportunities in FMCG, banking, infrastructure, technology, healthcare, and real estate. Strategic sector rotations and targeted investment positions will be essential for maximizing returns.
Long-Term Growth Prospects: Industries such as IT services, pharmaceuticals, and real estate show robust long-term growth potential, driven by digital transformation, healthcare demands, and urbanization.
The future of Indian equities looks promising, albeit with a need for careful navigation through the complexities of coalition politics and evolving economic policies. The government's commitment to increasing welfare spending, boosting manufacturing, and addressing rural distress provides a strong foundation for sustainable economic growth. However, the effectiveness of policy implementation and the ability to manage coalition dynamics will be critical determinants of market performance.
Investors can expect:
Resilient Growth: Sectors like FMCG, healthcare, and IT services are poised for resilient growth, supported by structural demand drivers and government initiatives.
Opportunities in Emerging Sectors: Renewable energy, electric vehicles, and advanced manufacturing offer exciting opportunities as the government prioritizes sustainability and innovation.
Volatility and Adaptability: While the market may experience volatility due to political and economic uncertainties, a well-diversified portfolio and adaptive investment strategies will be key to navigating these challenges.
Also Read:
Discover investment portfolios that are designed for maximum returns at low risk.
Learn how we choose the right asset mix for your risk profile across all market conditions.
Get weekly market insights and facts right in your inbox
It depicts the actual and verifiable returns generated by the portfolios of SEBI registered entities. Live performance does not include any backtested data or claim and does not guarantee future returns.
By proceeding, you understand that investments are subjected to market risks and agree that returns shown on the platform were not used as an advertisement or promotion to influence your investment decisions.
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Skip Password
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with Password →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with OTP →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Investor Profile Score
We've tailored Portfolio Management services for your profile.
View Recommended Portfolios Restart