by Sonam Srivastava
Published On March 5, 2023
Momentum investing is a popular strategy that has gained much attention recently. But did you know that Momentum Investing is a strategy that's not just decades but centuries old?
The strategy is based on the principle that stocks that have performed well in the past are likely to continue to perform well, and stocks that have performed poorly in the past are likely to continue to perform poorly.
In this blog post, we will explore the history of momentum investing and how it has evolved.
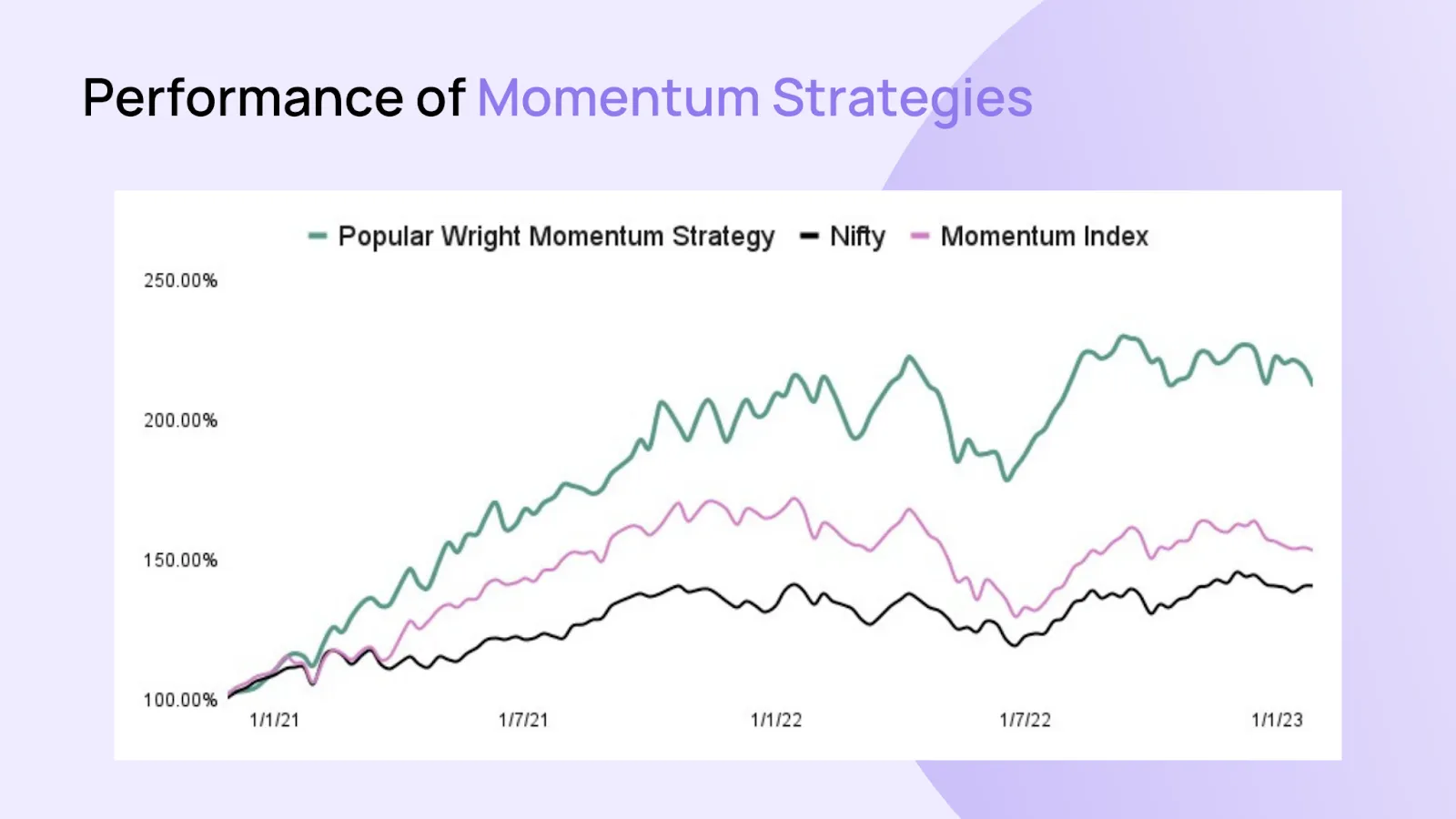
Momentum investing is an investment strategy that capitalizes on the recent price performance of assets. It involves buying assets that have exhibited strong upward price momentum and selling assets that have shown weak performance. The strategy is based on the belief that trends in asset prices tend to persist in the short term, and assets that have shown strength are more likely to continue rising, while those with weakness are more likely to continue declining. Momentum investing relies on quantitative analysis and relative strength comparisons to identify assets with positive or negative momentum. However, it's important to note that momentum investing carries risks, and careful risk management is necessary to navigate potential market reversals and volatility. Read What is Momentum Investing? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Momentum Investing .
The concept of momentum investing dates back to the 19th century when Charles Dow, the founder of the Dow Jones Industrial Average, observed that stock prices tended to move in trends. Dow believed that stocks that were rising in price were likely to continue to grow, and stocks that were falling in price were likely to continue to fall. This observation formed the basis of what we now know as momentum investing.
Momentum investing gained popularity in the 1990s when academic researchers Jagdish and Titman published studies showing that stocks that had performed well tended to outperform stocks that had performed poorly in the past. In addition, these studies found that momentum was a persistent and pervasive phenomenon that could be exploited to generate excess returns.

In the early days of momentum investing, the strategy was based on a simple buy-and-hold approach. Investors would buy stocks that had performed well in the past and hold them for an extended period, hoping that the momentum would continue.
Over time, however, momentum investing has evolved, and new strategy variations have emerged. One of the most popular variations is called "relative momentum" or "cross-sectional momentum." This strategy involves buying stocks that have performed well relative to other stocks in the same sector or industry. The idea is that even if the overall market is in a downtrend, there will always be some stocks that are outperforming their peers, and these are the stocks that the investor should focus on.
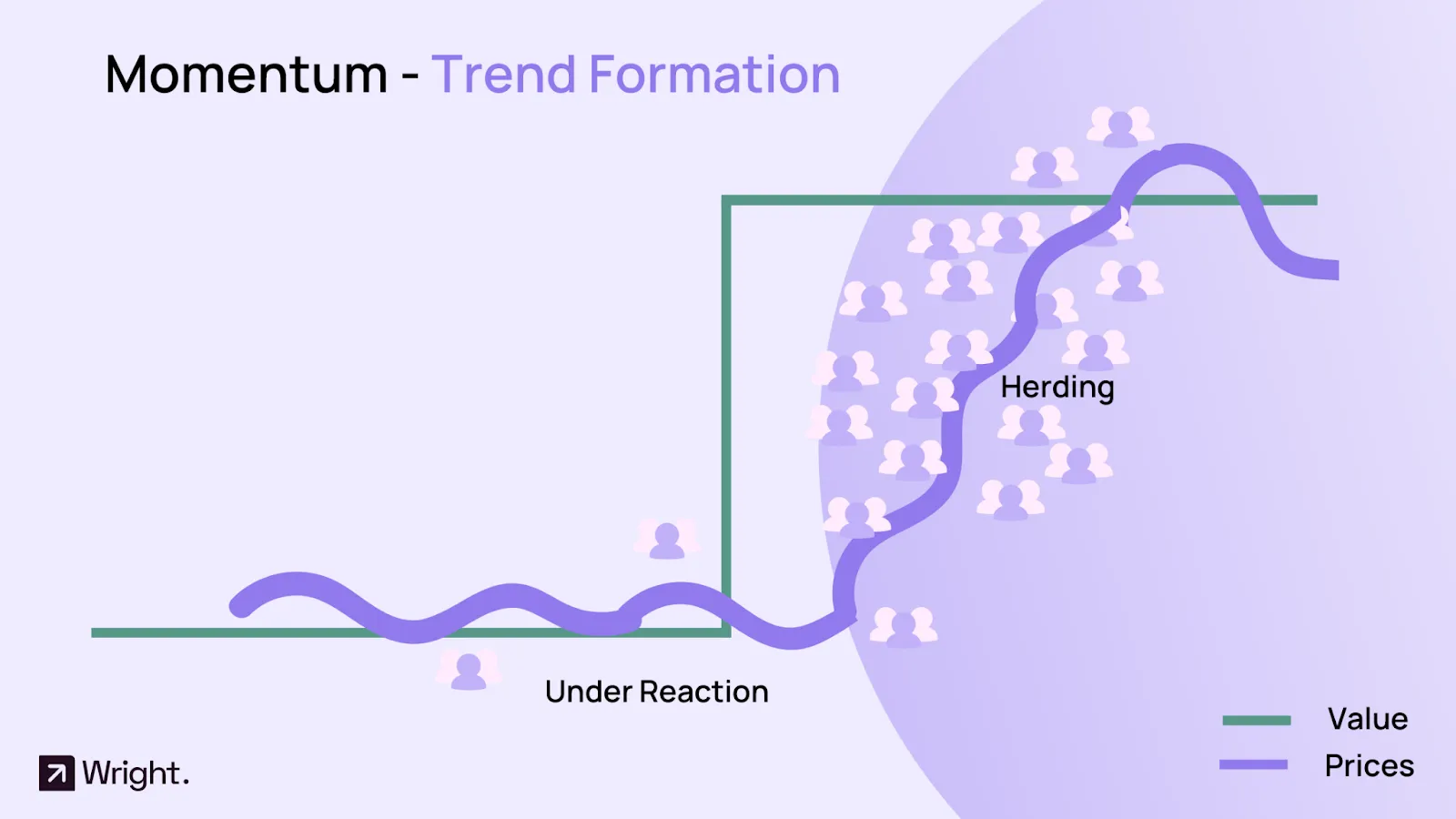
Another variation of momentum investing is called "time-series momentum." This strategy involves buying assets that have performed well over a specified period, such as the last 12 months, and shorting assets that have performed poorly over the same period. This strategy is designed to take advantage of trends that persist over time.
Momentum investing has become increasingly popular in recent years, and many investors now use the strategy as part of their overall investment approach.
The future of momentum investing appears bright for several reasons:
Increasing Availability of Data: With the growth of technology and the availability of big data, investors have access to vast amounts of information about stocks, sectors, and industries. This data can be used to identify trends and patterns that can help to identify momentum opportunities.
Evolution of the Strategy: As mentioned earlier, momentum investing has evolved, and new variations have emerged. These unique variations allow investors to take advantage of momentum in different ways, increasing the flexibility of the strategy.
Behavioural Finance: Behavioural finance has gained increased attention in recent years. Behavioural finance studies how investor behaviour can impact market trends and momentum. As investors become more aware of these behavioural biases, they may be better able to identify and exploit momentum opportunities.
Low-Cost Investing: With the rise of passive investing and the availability of low-cost investment options, investors can quickly and inexpensively build momentum-based portfolios. This ease of implementation makes momentum investing accessible to more investors.
Momentum trading can be categorized into two types: relative momentum and absolute momentum.
Relative momentum involves comparing the performance of different securities within a single asset class. Investors utilize this technique to identify which stocks to buy and sell. By assessing the relative performance of several securities within the same asset class, investors favor purchasing well-performing assets while selling poorly performing ones.
Absolute momentum strategies are commonly employed in trading. In an absolute momentum approach, the price behavior of a security is compared to its past performance over a specific time period. Momentum can be evaluated over longer time frames, such as weeks or months, or within shorter time ranges, like minutes or hours in day trading.
By considering both relative and absolute momentum, investors can tailor their trading strategies to capture opportunities based on the performance of securities within and across asset classes.
Potential for High Returns: Momentum investing aims to capture the continuation of trends in asset prices. By investing in assets that have shown recent strength and positive momentum, investors have the potential to benefit from continued price appreciation and achieve high returns.
Quantifiable and Objective Strategy: Momentum investing is based on quantitative analysis, focusing on observable price trends and performance metrics. This provides a systematic and objective approach to selecting investments, removing emotional biases from decision-making.
Diversification Benefits: Momentum investing can provide diversification benefits by identifying assets with uncorrelated price movements. By investing in assets from different sectors or regions that exhibit strong momentum, investors can reduce portfolio risk through diversification.
Opportunity for Active Trading: Momentum strategies often involve frequent buying and selling of assets based on short-term price trends. This presents opportunities for active traders to capitalize on market inefficiencies and potentially generate profits from shorter-term price movements.
Market Reversals and Whipsaws: Momentum investing relies on the continuation of trends in asset prices. However, markets can be unpredictable, and trends can reverse abruptly. Momentum strategies may result in losses if the momentum reverses before positions can be liquidated.
Behavioral Biases and Overtrading: Momentum investing requires disciplined execution and strict adherence to the strategy. Investors may be susceptible to behavioral biases, such as chasing past performance or being influenced by short-term market sentiment, which can lead to suboptimal decision-making and overtrading.
Limited Risk Management: Momentum investing may have limited risk management mechanisms. As the strategy primarily focuses on price trends, it may not adequately consider fundamental factors or valuation metrics, potentially exposing investors to overvalued assets or higher levels of risk.
Transaction Costs and Taxes: Frequent buying and selling associated with momentum strategies can result in higher transaction costs, including brokerage fees and bid-ask spreads. Additionally, short-term capital gains taxes may be applicable, reducing overall investment returns.
Limited Applicability in Efficient Markets: Momentum strategies tend to perform better in markets where trends and pricing inefficiencies exist. In highly efficient markets, where information is quickly incorporated into asset prices, the effectiveness of momentum investing may be reduced.
It's important for investors to carefully consider these advantages and disadvantages, along with their own risk tolerance and investment objectives, before implementing momentum investing strategies. Additionally, thorough research, risk management, and proper execution are crucial to mitigate potential drawbacks and enhance the likelihood of success.
Look no further than Wright’s Momentum strategy, one of the top-performing momentum strategies in the market. Wright Research has a manual mode enabling you to invest in the stocks directly without using the smallcase interface. The process is as follows:
Visit the Wright Momentum portfolio page . Click on “Get Started”
If the user is not logged it, the page will prompt you to login/signup. Post sign up enter your basic details, complete your basic risk profiling
All trades by default run through the smallcase interface. To do this manually, click on the Profile icon and select “Switch to Manual Based” mode
Click on “Subscribe Now” to proceed with subscription
Read through the Investment Advisor agreement and enter OTP details to accept the agreement
Select the payment plan that you are comfortable with and make the payment
Once you have subscribed, you will have access to the portfolio, its constituents and sector allocation
Here's a video guide to the manual subscription process
The process of investing in the Wright Momentum Smallcase is as follows:
Open a Brokerage Account: Smallcase is partnered with several leading brokers. You'll need to open a demat and trading account with one of these brokers such as Zerodha, Upstox, ICICI Direct, etc.
Visit the Smallcase Platform: Once your brokerage account is set up connect it to your smallcase account by visiting the Smallcase platform.
Select the Smallcase: In this case, you're interested in the Wright Momentum Smallcase . You will be able to search for this specific Smallcase on the platform.
Review and Purchase: Review the Smallcase to understand what it contains and if it aligns with your investment goals. If you decide to go ahead, you can buy Wright Momentum Smallcase directly on Smallcase.
Monitor and Manage Your Investment: After purchasing, you can monitor the performance of your Smallcase on the platform. You can also choose to rebalance the Smallcase as per the suggestions provided by the investment advisor you have subscribed to or add/remove individual stocks as per your preference.
What are the benefits of incorporating momentum investing in my portfolio?
Benefits of incorporating momentum investing include the potential for high returns, diversification benefits, a quantifiable and objective strategy, and opportunities for active trading.
How does momentum investing integrate with smallcase in India?
Smallcase, an investment platform in India, offers pre-built portfolios based on different investment strategies, including momentum investing. Investors can access momentum-focused smallcases that provide a convenient way to incorporate momentum strategies into their portfolio.
What are the risks and challenges associated with momentum investing?
Risks and challenges of momentum investing include market reversals and whipsaws, behavioral biases and overtrading, limited risk management, transaction costs and taxes, and limited applicability in efficient markets.
How can I implement momentum investing in my investment strategy?
To implement momentum investing, investors can identify assets with positive price momentum using technical analysis or quantitative models. They can then create a portfolio that focuses on buying assets with positive momentum and selling or avoiding assets with negative momentum.
Are there any specific momentum factors to consider in portfolio management?
Common momentum factors to consider include price momentum, relative strength, trend persistence, and volatility. The specific factors utilized can depend on the investor's strategy and the asset class being considered.
How does momentum investing perform in the Indian market?
The performance of momentum investing in the Indian market can vary. Historical studies have shown that momentum strategies can be successful in capturing trends and generating returns. However, market conditions, factors specific to India, and individual stock selection can impact the performance of momentum strategies in the Indian market. Thorough analysis and evaluation are necessary to assess the effectiveness of momentum investing in a specific market context.
Discover investment portfolios that are designed for maximum returns at low risk.
Learn how we choose the right asset mix for your risk profile across all market conditions.
Get weekly market insights and facts right in your inbox
It depicts the actual and verifiable returns generated by the portfolios of SEBI registered entities. Live performance does not include any backtested data or claim and does not guarantee future returns.
By proceeding, you understand that investments are subjected to market risks and agree that returns shown on the platform were not used as an advertisement or promotion to influence your investment decisions.
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Skip Password
By signing up, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with Password →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Log in with OTP →
By logging in, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy
"I was drawn to Wright Research due to its multi-factor approach. Their Balanced MFT is an excellent product."

By Prashant Sharma
CTO, Zydus
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
Answer these questions to get a personalized portfolio or skip to see trending portfolios.
(You can choose multiple options)
Investor Profile Score
We've tailored Portfolio Management services for your profile.
View Recommended Portfolios Restart